Overview
Built-in Engines
Currently, Tachybase supports the following built-in engine types:
A local storage engine is automatically added during system installation and can be used directly. You can also add new engines or edit existing engine parameters.
Engine Common Parameters
In addition to the specific parameters for different engine types, the following are common parameters (using local storage as an example):
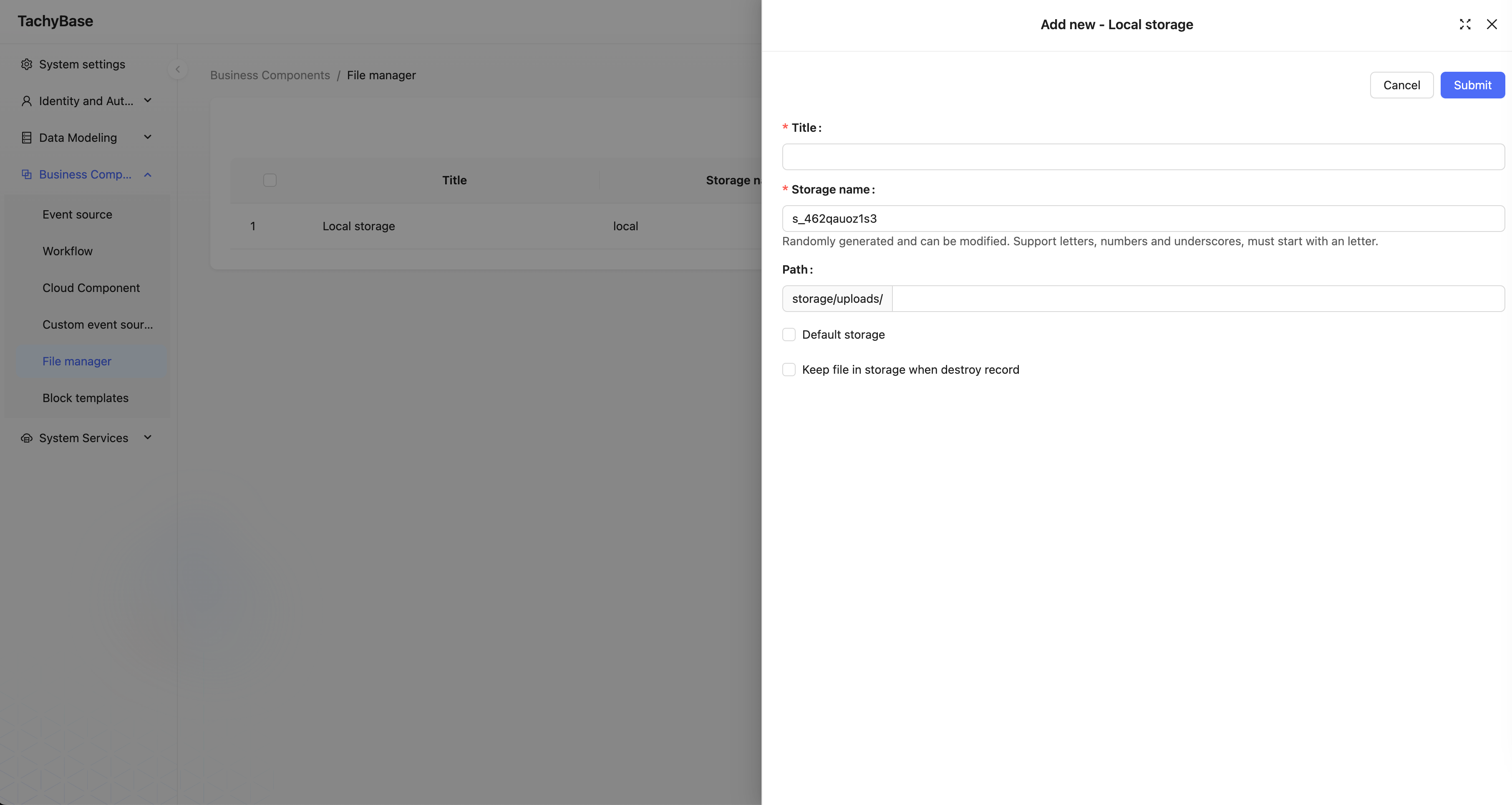
Title
The name of the storage engine, used for human identification.
System Name
The system name of the storage engine, used for system identification. It must be system-unique; if not filled, the system will automatically generate it randomly.
Base Access URL
The URL prefix for external access to the file, which can be a CDN access URL base, such as: "https://cdn.Tachybase.com/app" (no trailing "/" needed).
Path
The relative path used when storing files. This part will also be automatically concatenated to the final URL during access. For example: "user/avatar" (no leading or trailing "/" needed).
File Size Limit
The size limit for uploading files to this storage engine. Files exceeding this size cannot be uploaded. The system default limit is 20MB, adjustable up to a maximum of 1GB.
File Type
You can restrict the types of files that can be uploaded using MIME type syntax. For example: image/* represents image files. Multiple types can be separated by commas, such as: image/*, application/pdf allows image types and PDF type files.
Default Storage Engine
When checked, it is set as the system's default storage engine. When attachment fields or file collections do not specify a storage engine, uploaded files will be saved to the default storage engine. The default storage engine cannot be deleted.
Keep Files When Deleting Records
When checked, uploaded files in the storage engine are retained when data records in the attachment table or file table are deleted. By default, this is unchecked, meaning files in the storage engine will be deleted when records are deleted.
After a file is uploaded, the final access path will be composed of several parts:
https://cdn.tachybase.com/app/user/avatar/20240529115151.png
