SchemaSettings
After activating UI configuration, when the mouse moves over specified blocks, fields, or actions, the corresponding Schema toolbar will be displayed. The settings button in the toolbar is the settings controller for the current Schema.
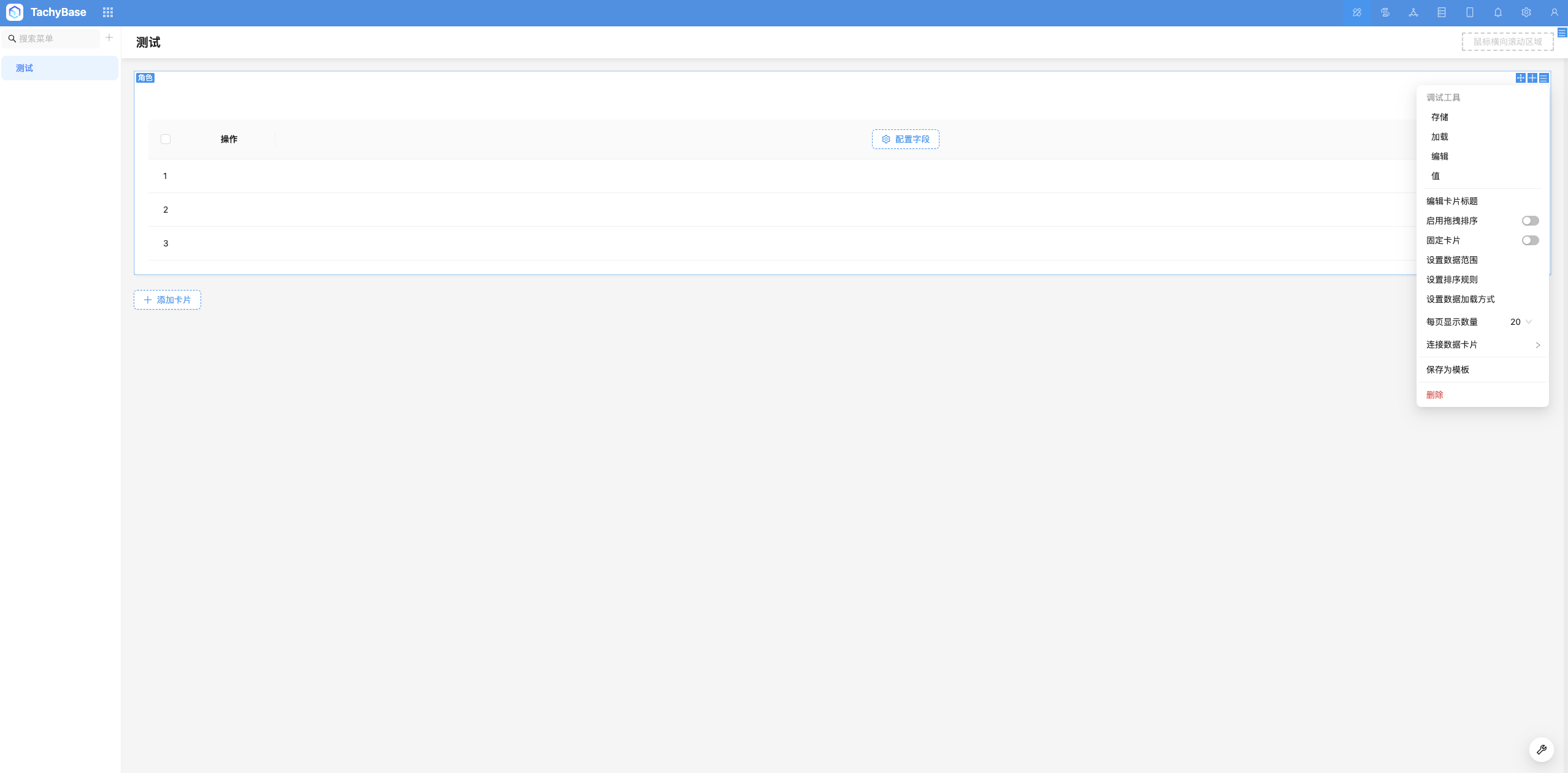
Purpose of SchemaSettings
SchemaSettings modifies properties of FieldSchema or Field, and components read these properties to implement configuration for blocks, fields, actions, etc.
Field is an instance of FieldSchema. Modifying Field will not save the Schema structure to the database, it only modifies the properties of the current instance and will be lost after refreshing the page. If you need to save to the database, you need to modify FieldSchema.
Built-in Settings Controllers

Add Settings Items to Existing Settings Controllers
It's recommended to use the schemaSettingsManager.addItem() method to add settings items. For detailed item configuration, refer to SchemaSettings Item API
Add New Settings Controller
For detailed SchemaSettings parameters, refer to SchemaSettingsOptions API
Add in Plugin load Method
It's recommended to use schemaSettingsManager.add() to add the new settings controller to the application
How to Use the Newly Added Settings Controller
The added SchemaSettings can be used in the x-settings parameter of Schema. Not all components support x-settings, usually need to be used in combination with wrapper components like BlockItem, FormItem, CardItem. In custom components, you can also use useSchemaSettingsRender() to handle x-settings rendering independently.
In most scenarios, x-settings needs to be used in combination with wrapper components like BlockItem, FormItem, CardItem. For example:
If wrapper components like BlockItem, FormItem, CardItem do not meet the requirements, you can also use useSchemaSettingsRender() to handle x-settings rendering.
In most scenarios, settings are placed on SchemaToolbar, so supporting x-toolbar for custom components can indirectly support x-settings. For more usage, refer to Schema Toolbar
How to Implement Schema Settings?
Use useSchemaSettings() to get the current Schema's Designable, and use Designable to operate on Schema. Commonly used APIs include:
dn.insertAdjacent() dn.getSchemaAttribute() dn.shallowMerge() dn.deepMerge() dn.findOne() dn.find() dn.remove() dn.remove()

